Préserver l’environnement avec une maison zéro énergie
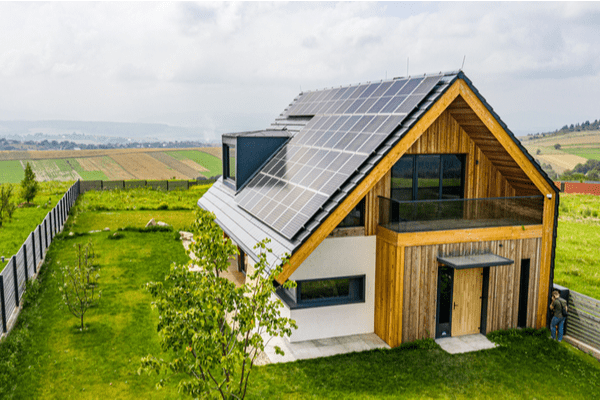
Une maison zéro énergie, qu’est-ce que c’est ?
Maison passive, maison BBC, bâtiment à énergie positive (BEPOS) ou encore maison zéro énergie, les termes pour désigner les maisons économes en énergie sont légion et il est parfois difficile de les différencier. La maison zéro énergie, par exemple, est-elle un logement au besoin énergétique nul ou bien une habitation n’utilisant aucune énergie fossile, néfaste pour l’environnement ? Dans ce guide, nous avons pour objectif de mettre en lumière ce concept et ses enjeux. Peut-être pourrez-vous, vous aussi, vous lancez dans un projet de construction de maison zéro énergie. Suivez le guide.
Maison zéro énergie : la définition concrète
Par nature, une maison zéro énergie est une habitation dont les besoins énergétiques sont très réduits, tant et si bien qu’ils sont entièrement compensés par l’énergie renouvelable implémentée dans le logement. On estime que dans une habitation de ce type, la consommation d’énergie primaire liée aux postes de dépenses principaux (chauffage, ECS, éclairages, auxiliaires, etc.) est limitée à 15 kWh/m².an, et que la consommation tous types de postes confondus (y compris l’usage des appareils électriques) est au maximum de 100 kWh/m².an.
Utopie ou réalité ? En fait, à l’ère de la réglementation thermique et environnementale 2020 (RT 2020), ce type de construction tend à devenir la norme. Pourquoi ?
Tout simplement pour préserver notre environnement et maîtriser au possible les changements climatiques mondiaux advenant en ce moment. Avec les transports, le secteur du bâtiment est l’un des plus énergivores. Le niveau d’énergie nécessaire à l’éclairage ou encore au chauffage des habitations notamment, est colossal et responsable de la plupart des émissions de gaz à effet de serre. Pour pallier au possible le phénomène, deux axes majeurs sont envisagés par les gouvernements européens :
- Procéder à une rénovation énergétique massive des logements, pour éradiquer les passoires énergétiques : améliorer les performances des logements permet de limiter l’utilisation d’énergies fossiles.
- Inciter à la construction de maisons très performantes comme la maison zéro énergie, via des politiques et des normes strictes conditionnant le secteur de la construction.
Comment construire une maison zéro énergie ?
Une architecture bioclimatique caractéristique de la maison zéro énergie
Vous vous demandez peut-être comment la maison zéro énergie est bâtie et dans quelle mesure elle implique des besoins réduits en énergie. En fait, arriver à cet état de fait nécessite de penser la conception bioclimatique de l’habitation. Il s’agit en fait de bâtir les plans de la maison en prenant en compte son environnement direct : nature du sol et des couches profondes et superficielles, végétation déjà présente (laquelle fournit de l’ombre à l’habitation), orientation générale du terrain, caractéristiques climatiques, de vents, d’altitude…
L’architecture bioclimatique de la maison zéro énergie lui permet de bénéficier naturellement du meilleur apport de lumière dans les pièces de vie, d’ombre là où c’est nécessaire ou encore d’un parfait système de ventilation naturelle ne demandant l’utilisation d’aucune source d’énergie. Ce type de construction n’impacte donc pas non plus le milieu environnant, avec lequel elle est plutôt en osmose.
Résultat ? Le besoin en chauffage, en eau chaude sanitaire, en électricité, en climatisation ou en ventilation est parfaitement réduit, même pour un ménage nombreux aux besoins énergétiques lourds et ce tout au long de l’année.
Des équipements performants fonctionnant aux énergies renouvelables
Là où certains détracteurs pointent du doigt la faible efficacité de certains appareils du renouvelable dans certains contextes (ménage trop grand, aléas climatiques, etc.), tous s’accordent à dire que ces appareils fonctionnent parfaitement bien pour couvrir jusqu’à 70 % des besoins énergétiques des ménages français. Or, la demande en énergie est réduite au strict minimum dans une maison zéro énergie ! Les appareils renouvelables que sont la pompe à chaleur air air, air eau, ou eau eau, ainsi que les panneaux solaires ou les appareils à biomasse individuelle ont donc largement le potentiel pour combler ces besoins.
Ce faisant, il n’est aucunement nécessaire de solliciter la résistance électrique d’appoint de ces appareils. La maison utilise 100 % de ses ressources renouvelables et bénéficie de ce fait du meilleur confort thermique, été comme hiver. En ne rejetant pas de gaz à effet de serre dans l’atmosphère, la maison est parfaitement économe et sans impact sur l’environnement, d’autant plus lorsqu’elle est bâtie à partir d’un maximum de matériaux biosourcés.
Note : une maison zéro énergie est bien évidemment écologique, mais elle est aussi très économique ! Les factures énergétiques des occupants est quasiment inexistante, ce qui permet à tout un chacun d’envisager ce type de construction. Vous paierez plus cher à l’achat, mais gagnerez réellement d’argent sur vos coûts d’usage. Ce genre d’habitation est également facilement valorisable dans le cadre d’une vente immobilière. Il n’y a plus à hésiter !
Pour construire votre maison zéro énergie, n’hésitez pas à vous tourner vers un constructeur spécialisé en la matière. Bien des entreprises prôneront des constructions écologiques : en réalité, la conception bioclimatique est un métier à part entière, qui nécessite de s’adresser uniquement à des professionnels dont l’offre y est 100 % dédiée.
